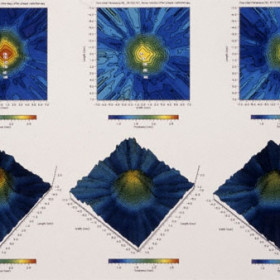
3D ultrasound
3D ultrasound used to create topographic renderings of choroidal melanoma regression after palladium-103 plaque radiation therapy
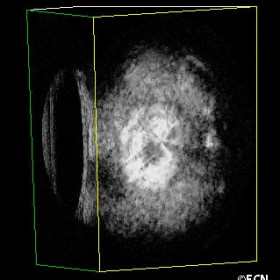
3D ultrasound demonstrates the back of the plaque
3D ultrasound demonstrates the back of the plaque and the tumor in different planes of section.
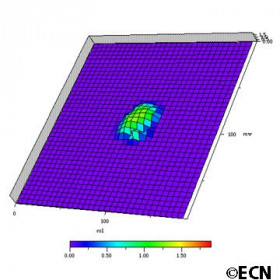
3D ultrasound generated topographic map
3D ultrasound generated topographic map of a juxtapapillary melanocytoma
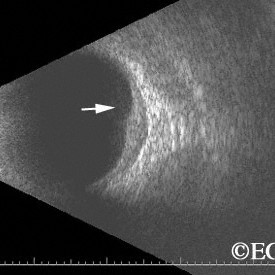
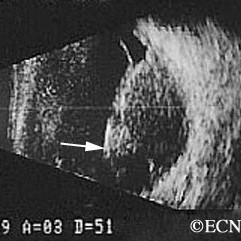
Brawny scleritis
Brawny scleritis - 10 MHz B-scan ultrasound reveals thickening of the sclera and vitreous cells (arrow).
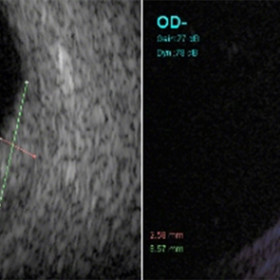
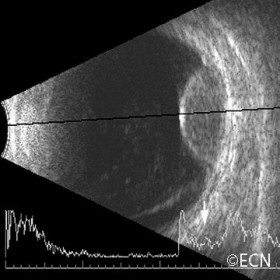
Choroidal Hemangioma
Choroidal Hemangioma - Moderately high internal reflectivity and a "dome" shape are typically revealed by ultrasound imaging of choroidal hemangioma.
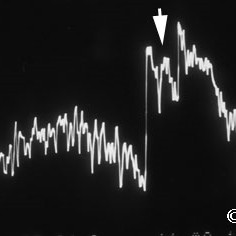
Choroidal hemangioma
Choroidal hemangioma - A-scan reveals high internal reflectivity within the tumor (arrow).
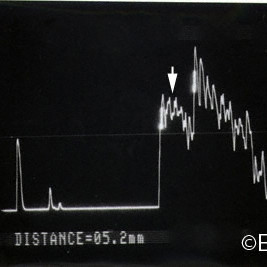
Choroidal hemangioma
Choroidal Hemangioma- A-scan image reveals characteristically high internal reflectivity (arrow) and an apical height of 5.2 mm.
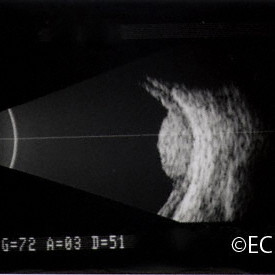
Choroidal hemangioma
Choroidal Hemangioma- 10 MHz B-scan of a circumscribed choroidal hemangioma reveals the hyperechoic - highly reflective tumor
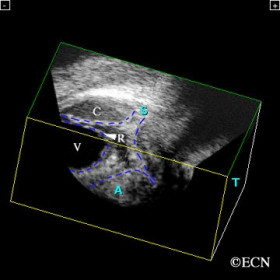
Choroidal Hemorrhage
Choroidal Hemorrhage- Interactive 3D ultrasound imaging is particularly helpful in evaluation of disorganized eyes.
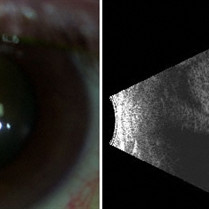
Choroidal Melanoma
Choroidal Melanoma: Left, a slit lamp photograph demonstrates the anterior edge of the choroidal melanoma. Right, a corresponding 10 MHz B-scan reveals a large choroidal melanoma beneath a closed funnel retinal detachment.
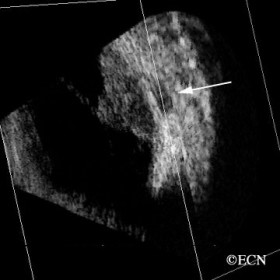
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma - 3D ultrasound demonstrates retrobulber extrascleral tumor extension (arrow) in both axial and coronal sections.
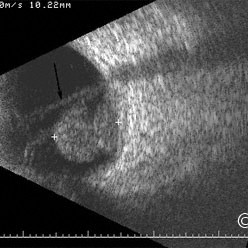
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal Melanoma- 10 MHz B-scan reveals a collar button shpaed choroidal melanoma beneath an open funnel retinal detachment.
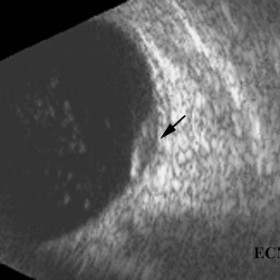
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal Melanoma- 10 MHz B-scan ultrasound reveals choroidal excavation (arrow) at the base of this melanoma.
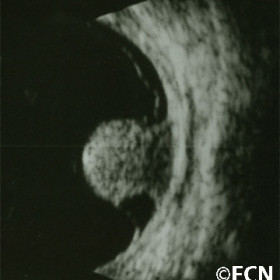
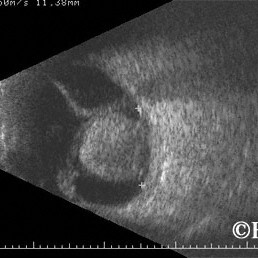
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma- Collar button also called mushroom shaped
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma- Dome shaped with secondary retinal detachment (3D ultrasound reconstruction)
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma- Dome shaped with retinal detachment. Low internal reflectivity seen on interpolated A-scan (arrow).
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal Melanoma- 10 MHz B-scan reveals a mushroom shaped choroidal melanoma beneath a total retinal detachment.
Choroidal melanoma
Choroidal melanoma- 10 MHz B-scan reveals a mushroom shaped tumor extension (arrow).
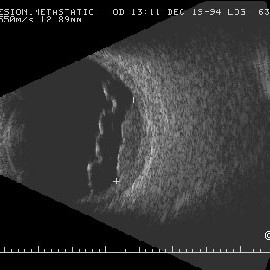
Choroidal metastasis 10 MHz B-scan
Choroidal metastasis 10 MHz B-scan image. Note the irregular surface, overlying retinal detachment, and variable internal reflectivity.
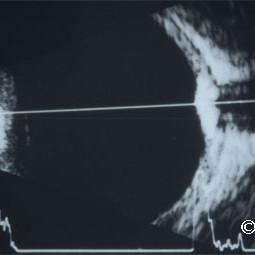
Choroidal osteoma
Choroidal osteoma and its associated orbital shadowing (arrow).
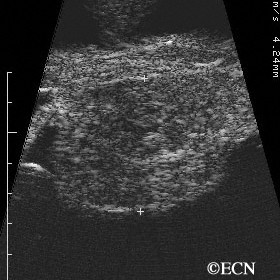
Ciliary body melanoma
Ciliary body melanoma - 20 MHz B-scan demonstrates the relatively hypoechoic tumor with no extension through the iris.
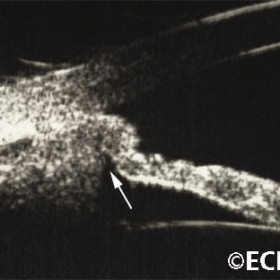
Ciliary body melanoma
Ciliary body melanoma - note the iris displacement and erosion of the iris pigment epithelium (arrow).
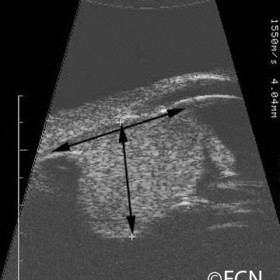
Ciliary Body Melanoma
Ciliary Body Melanoma- 20 MHz B-scan reveals a collar-button shaped ciliary body melanoma (this technique is used to measure tumor size).
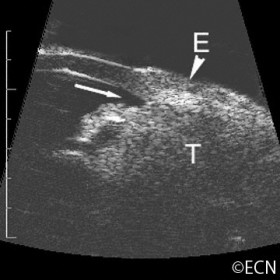
Ciliary body melanoma
Ciliary body melanoma (T) with extrascleral extension (E) 20-MHz ultrasound- Note the thinning of the highly reflective sclera
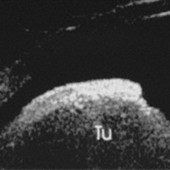
Ciliary body melanomas
Ciliary body melanomas and how they can affect their anterior segment. Left: disinsertion of the iris root, Middle: Mass effect pushing the iris anteriorly, Right: erosion of the iris pigment epithelium.
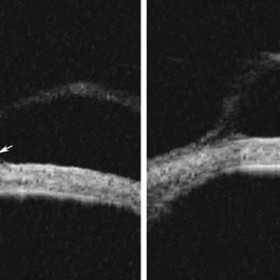
Epibulbar Conjunctival Cyst
Epibulbar Conjunctival Cyst - 35 MHz High frrequency ultrasound (see conjunctival tumor images for correlation).
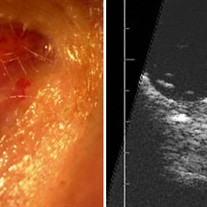
Epibulbar squamous carcinoma
Epibulbar squamous carcinoma 20 MHz B-scan- There is no evidence of intraocular invasion (blunting of the angle or thickening of the ciliary body and uvea).
Eyelid Hydrocystoma
Eyelid Hydrocystoma - Left, a slit lamp photograph demonstrates a pigmented hydrocystoma (simulating a melanoma). Right, a 20 MHz high frequency ultrasound demonstrates that it is cystic.
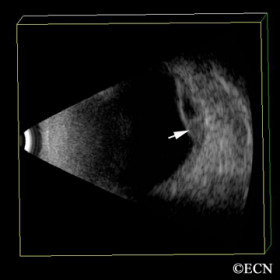
Hemorrhagic choroidal detachment
Hemorrhagic choroidal detachment - 3D ultrsound reveals a diagnostic blood - serum level (arrow)
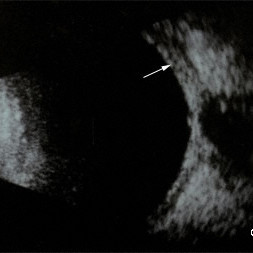
Infiltrative choroidopathy
Infiltrative choroidopathy (10 MHz ultrasound) - Note the choroidal thickening (arrow), also widening of the optic nerve shadow and papilledema.
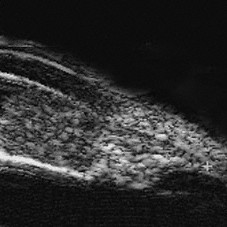
Iridociliary melanoma (20 MHz ultrasound)
Iridociliary melanoma (20 MHz ultrasound) - Note the low-reflective tumor extending into the supraciliary space.
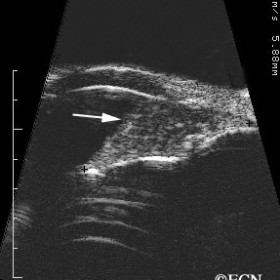
Iridociliary melanoma
Iridociliary melanoma - 20 MHz B-scan reveals a hypoechoic tumor filling the angle and supraciliary space, with posterior displacement of the iris pigment epithelium.
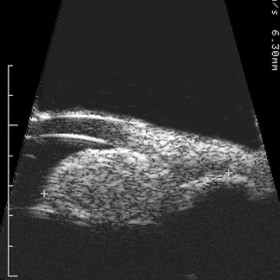
Iris Melanocytoma
Iris Melanocytoma - 20 MHz B-scan reveals a relatively hyperechoic iris tumor. Note the tumor extends into the ciliary body and obscures the iris pigment epithelium.
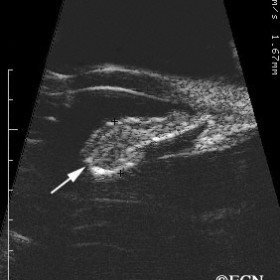
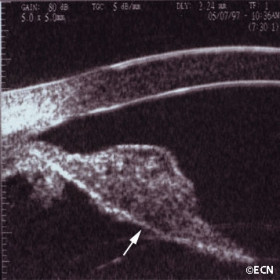
Iris Melanoma
Iris Melanoma - 20 MHz B-scan reveals a hypoechoic tumor extending through the iris pigment epithelium (arrow).
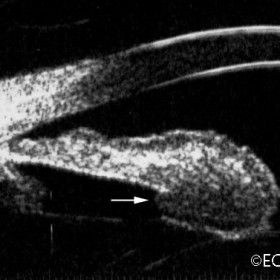
Iris Melanoma
Iris Melanoma - High frequency (50 MHz) image- Note hypo-echoic tumor eroding through (arrow) the iris pigment epithelium.
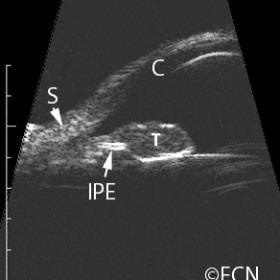
Iris Melanoma
Iris Melanoma - 20 MHz B-scan demonstrates how the tumor (T) can break through and destroy the hyperechoic iris pigment epithelium (IPE).
Iris Melanoma
Iris melanoma (50 MHz ultrasound image)- Note the low reflective tumor has broken through the iris pigment epithelium (arrow).
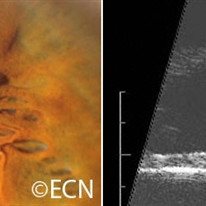
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst
Iris Pigment Epithelial Cyst - This unusual pupillary cyst (left) is demonstrated to be acoustically hollow on a transverse 20 MHz B-scan examination (right).
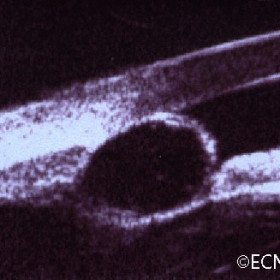
Iris stromal cyst (50-MHz ultrasound)
Iris stromal cyst (50-MHz ultrasound) - Not that the iris stroma has been obliterated and the pigment epithelium is displaced posteriorly.

Metastatic choroidal tumor
Metastatic choroidal tumor - Wilm`s origin, note the variable internal tumor reflectivity and retrobulbar edema (arrow).
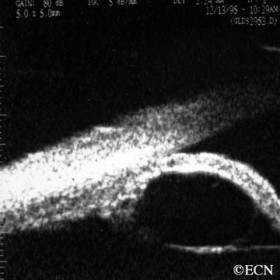
Neuroepithelial iris cyst
Neuroepithelial iris cyst - High frequency 50 MHz ultrasonography demonstrates the cyst (at the iris root) anteriorly displacing the iris stroma causing focal angle closure.
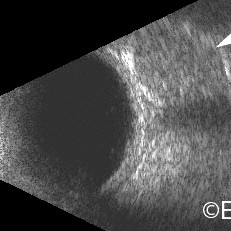
Orbital Hemangioma
Orbital Hemangioma - 10 MHz B-scan reveals a relatively low reflective ovoid intraconal tumor in contact with the optic nerve.
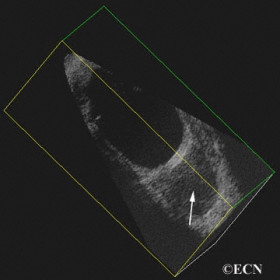
Orbital Lymphoma
Orbital Lymphoma - 3D ultrasound is used to display this retrobulbar lymphoma (arrow) in two planes of section.
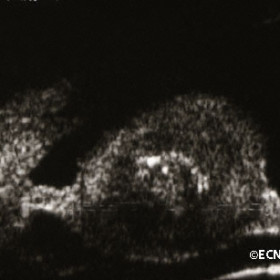
Pearl cyst
Pearl cyst - High frequency 50 MHz B-scan ultrasound reveals 3 cyst layers.

Retinal Detachment
Retinal Detachment - 3D ultrasound can be used to create and scroll through successive coronal sections of a retinal detachment (in evaluation of subretinal traction:tumors).
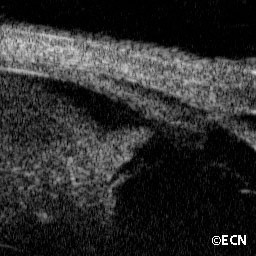
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma - high frequency ultrasound of anterior extension
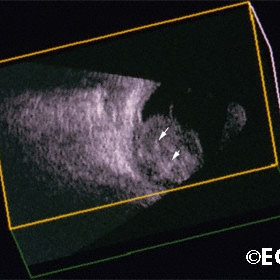
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma- Large tumor as seen in a 3D ultrasound block demonstrates calcium (arrows).
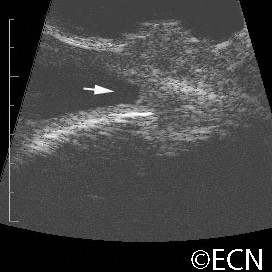
Squamous carcinoma with intraocular invasion
Squamous carcinoma with intraocular invasion - Note the blunted angle (arrow).
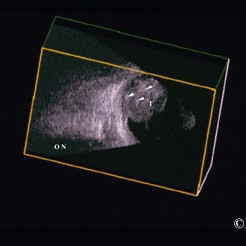
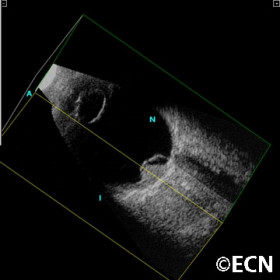
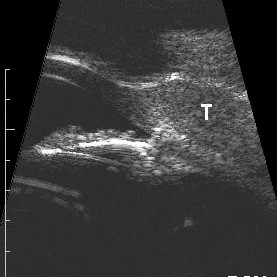
3D ultrasound of a retinoblastoma
Three-dimensional ultrasound of a retinoblastoma. Note the calcifications (arrows) within the tumor [T}. The optic nerve [ON] is not involved.