Description
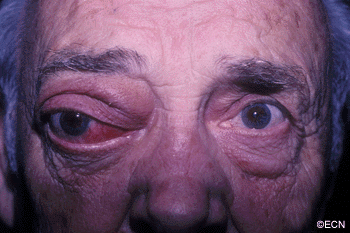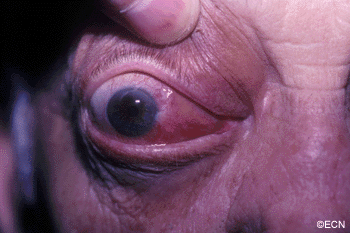
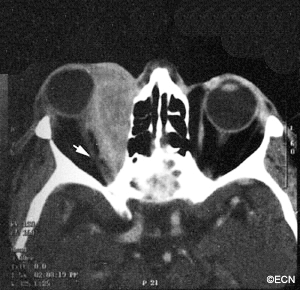
Sclerosing orbital pseudotumor is uncommon. Due to unknown reasons, these tumor behave differently than other types of pseudotumor of the orbit. They grow more slowly, cause less pain, and are characterized by scarring (hardening of the tumor tissue).
Symptoms
Sclerosing orbital pseudotumor is not cancer. But, by local growth it can cause bulging of the eye (proptosis), double vision (diplopia) and loss of vision. Sclerosing orbital pseudotumor can (rarely) extend into the sinuses, brain, and other orbit.
Diagnosis
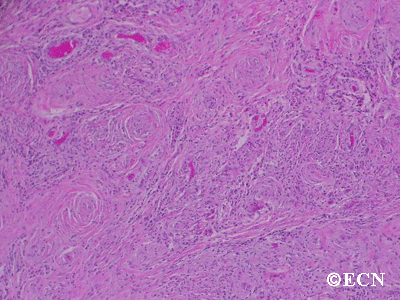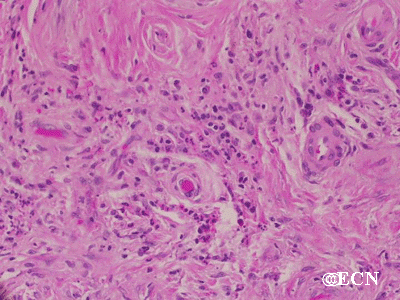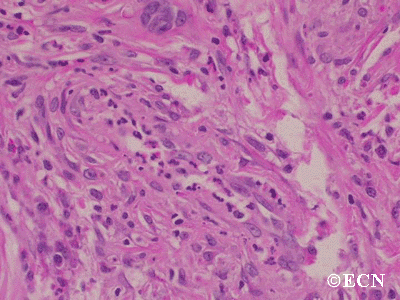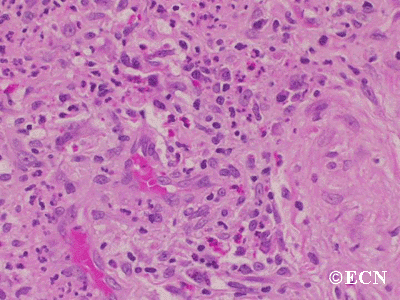
Sclerosing orbital pseudotumor is usually diagnosed by biospy (orbitotomy).
Once the diagnosis is confirmed by pathology, systemic testing to rule out specific infectious and inflammatory causes should be performed. For example, an ANCA blood test and a chest x-ray should be performed to rule out Wegener’s Granulomatosis. Many of these patients have a past medical history of sinusitis, sinus surgery, or inhalation drug abuse. Therefore, concurrent treatable sinus disease should be addressed.
Treatments
Sclerosing orbital pseudotumors are less responsive to steroid therapy. Most cases are treated with combinations of surgery, steroid therapy, radiation and chemotherapy depending upon the clinical picture and the patient’s response to treatment.