Choroidal Melanoma
By Paul T. Finger, MD
Description
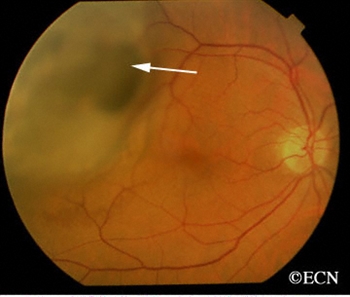
The wall of the eye has 3 main layers. From outside to inside there is: the white sclera, a blood vessel layer called the uvea (choroid, ciliary body and iris) and an inner retinal layer. Further, the pigment producing cells, “melanocytes” are primarily found in the vascular uveal layer. It is those melanocytes that can turn into malignant melanoma. Therefore, when melanoma happens in the choroid, they are called “choroidal melanoma,” the most common primary intraocular malignancy in adults. That said, choroidal melanomas are rare with 5 to10 out of each million people diagnosed with a choroidal melanoma each year. Choroidal melanomas can spread to other parts of the body.
Eye cancer specialists can determine if you have a choroidal melanoma by performing a complete eye examination with testing. This includes asking questions about your medical history, examining both of your eyes, looking into the eye through a dilated pupil, performing an ultrasound examination, and specialized photography (to examine the circulation within the choroidal melanoma).
MOST – Fingers’ Melanoma Mnemonic
Dr. Finger has developed the mnemonic device “MOST” to help eye care specialists to determine if the intraocular tumor is a melanoma.

“M,” Melanoma:
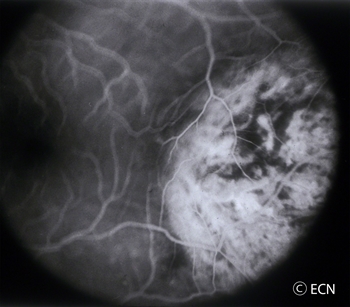
- “O,” Orange Pigment Lipofuscin (OPL) a metabolic side product of cell death. This finding tells us that that either the underlying tumor is destroying the overlying tissue or itself is degenerating. Lipofuscin is best seen with a photographic test called Fundus Auto Fluorescence imaging, or FAF.
- “S,” Subretinal fluid (SRF) is created by poorly formed or new, “neovascular” blood vessels within the tumor. Cancers need new vessels in order to grow. Large amounts of SRF can be seen by ophthalmoscopy (looking into the eye) and ultrasound imaging. However, small amounts of SRF are best seen on 3D optical coherence tomographic imaging (3D-OCT).
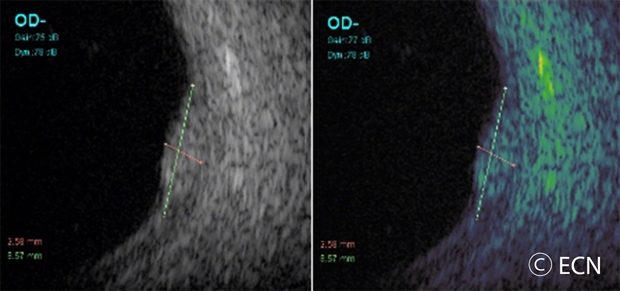
- “T,” Thickness of the tumor has been associated with malignancy. Simply, the thicker it is the more likely a pigmented intraocular tumor is malignant. It is widely accepted that tumors greater than 2.0 mm are more likely to be malignant. Ultrasound imaging is currently the best method to measure tumor thickness.
Your specialist will also request that you have a complete general medical check up and specific tests depending upon what they see inside your eye. In the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study (COMS), participating eye cancer specialists correctly diagnosed select choroidal melanoma in over 99.6% of cases (without a biopsy). That said, patients with unusual appearing “atypical” tumors were not entered into the study.
Classic Indications for Biopsy
Atypical tumor, metastatic tumor with no observable primary cancer and when the patient requests a pathology diagnosis. More recently, primarily due to genetic testing services, more and more centers are routinely performing choroidal tumor biopsy primarily for genetic tumor analysis. Genetics offers information about the tumor, but does not allow doctors to avoid treatment or follow up systemic testing for metastasis.
Choroidal biopsy has been associated with a risk of hemorrhage, infection, retinal detachment and a poorly quantified risk of tumor seeding (outside the eye). Risks related to tumor seeding are thought to be small, but clearly they have not been evaluated by any large prospective or retrospective study. Each eye cancer specialist should discuss the relative risks (known and unknown) of biopsy prior to surgery.
Questions About Intraocular Biopsy:
-
- Remove the need for surgical tumor treatment?
- Reduce the number of radiologic examination or years needed for systemic surveillance?
- What are the risks of biopsy (hemorrhage (e.g. vitreous, subretinal, subfoveal), seeding, damage to the lens, optic nerve, retinal detachment, cataract, epiretinal membrane, loss of vision, loss of eye and/or reaction to anesthesia).
Symptoms
Most choroidal melanoma patients have no symptoms. The melanoma is found on routine eye examination. If patients have choroidal melanoma symptoms, they are usually seeing “flashes of light,” noticing “distortion” or loss of vision, and floating objects (floaters) in their vision.
-
- If the choroidal melanoma is in the front of the eye (near the natural lens), it can push or tilt the natural lens causing an irregular astigmatism (blurring of vision).
- Choroidal melanoma can leak fluid beneath the retina, making the retina detach and cause symptoms of flashing lights and floating specks “floaters”.
- If the choroidal melanoma is in the macula (center of vision), it can grow beneath the fovea making the patient far-sighted. The choroidal melanoma can also grow into and destroy the fovea causing distortion, loss of vision or changes in color perception.
It is important to note that most patients with choroidal melanoma have no symptoms at all. Their tumors are found when they visit their eye doctor for a “routine” eye examination. So everyone should have periodic eye examinations (including dilated ophthalmoscopy). In general, the earlier and smaller the choroidal melanoma, the better the prognosis for both life and sight.
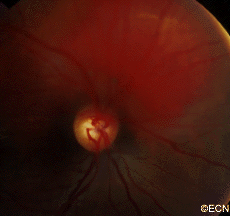
Other, more unusual presentations of anterior choroidal and iridociliary melanoma are discoloration of the iris, a brown spot on the outside of the eye, an irregularly shaped pupil and glaucoma.
Diagnosis
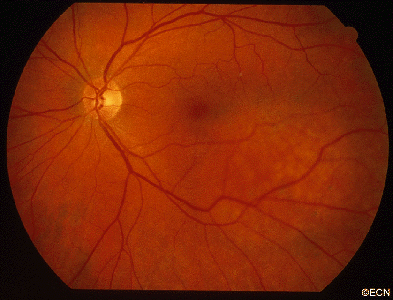
Choroidal melanoma is usually seen by ophthalmoscopy (when your eye doctor looks through a lens into your dilated pupil). Choroidal melanoma has typical “diagnostic” characteristics that include but are not limited to: pigmentation, low to moderate internal ultrasound reflectivity, clumps of orange pigment lipofuscin on its surface, leakage of subretinal fluid, or retinal detachment (on or around the choroidal melanoma) and thickness.
-
- Pigmentation is due to naturally occurring melanin that comes from melanocyte cells in the choroidal layer of the eye. Choroidal melanomas are most commonly pigmented, but can be variably pigmented and even non-pigmented (amelanotic). Non-pigmented choroidal melanoma is due to a proliferation of melanocytes that have lost their ability to make the melanin pigment.
- Orange pigment is made up of a chemical called lipofuscin and appears on the surface of choroidal melanomas. Lipofuscin is a product of cell death which indicate that cells are dying on the tumor’s surface. This is also sign of metabolic activity. Melanomas are more metabolically active than choroidal nevi.
- Ultrasound is typically used to measure the choroidal melanoma size, evaluate internal tumor reflectivity, and look for melanoma extension behind the eye into the orbit called extrascleral extension. Ultrasound imaging has demonstrated that most choroidal melanomas are shaped like a dome and less commonly like a mushroom. Ultrasound can also evaluate and detect choroidal melanoma associated retinal detachment. However, optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a more sensitive way to detect subretinal fluid – retinal detachment.
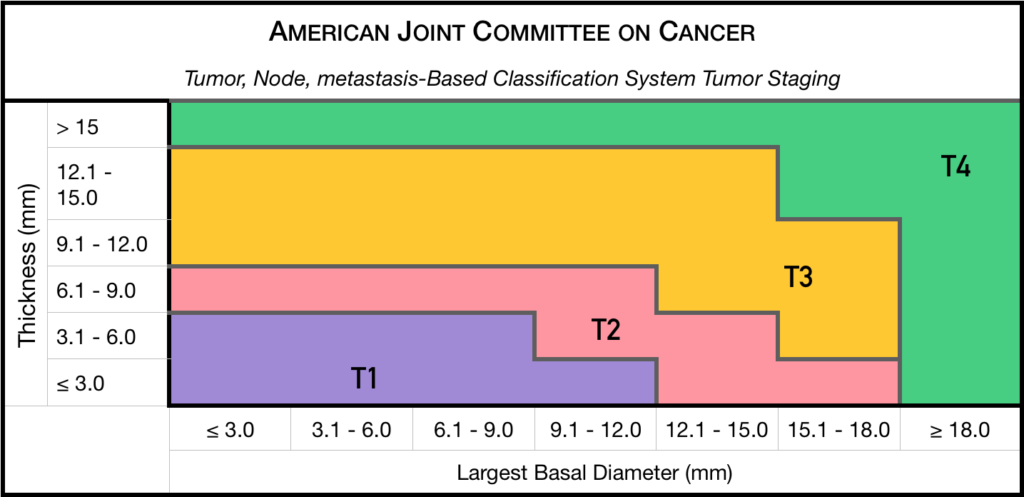
Staging
Chaired by Dr. Paul T. Finger, a committee of top ophthalmic specialists assembled to form the AJCC-UICC Ophthalmic Oncology Task Force. To ensure a broad range of specialists, Dr. Finger “internationalized” the committee, including over 58 members both from the USA and around the world.
This committee had one driving goal: to design a clinically useful Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) based classification “language” for ocular tumors. This first-of-its-kind classification system has become a universal language for all who diagnose and treat ocular tumors.
Not only does a universal classification system offer cancer staging for the patient, it also allows physicians to directly compare data. In the long run, a common “eye tumor” language helps us determine and differentiate treatment types as well as coordinate the efforts of researchers working for a cure.
Dr. Finger has since translated this staging system for the worlds’ Union International for Cancer Control (UICC), and offered it to the world. In order to get everyone to employ this new language, he has recruited all the major medical journals to require eye cancer researchers to use AJCC-UICC staging.
Treatments
Small Choroidal Melanoma (AJCC T1 and T2):
Patients with a small choroidal melanoma can be treated after their first visit, but since growth helps to prove that the tumor is a cancer, your doctor may suggest “observation” or watching for a small amount of choroidal melanoma growth prior to treatment. Your eye cancer specialist should discuss the relative risks and potential benefits of “observation for growth” as compared to “immediate treatment” for choroidal melanoma. If growth is documented (typically within 6 months of observation), eye cancer specialists will typically recommend definitive treatment.
Medium-sized Choroidal Melanoma (AJCC T3 and T4):
Most patients with large-sized choroidal melanoma can be also be treated with eye-sparing low energy radiation therapy (e.g. palladium-103). However, larger tumors require more radiation and larger irradiated intraocular volumes resulting in greater risk of radiation side-effects and poor vision. Rarely such eyes have to be secondarily removed. Eye cancer specialists try to preserve eyes, even if the eye had reduced vision.
Large-sized Choroidal Melanoma:
Very large choroidal melanomas (greater than 22 mm width) may be treated by initial removal of the eye (enucleation). This is because the amount of radiation required to destroy a choroidal melanoma that fills most of the eye will likely be too much for the eye to tolerate.
However, most patients, even with very large-sized choroidal melanoma can be treated with eye-sparing radiation therapy. However, after eye sparing radiation for very large choroidal melanomas, eyes are at greater risk to have poor vision, secondary inflammation and may require secondary removal at a later date.
Additional Info
Patients often ask why they have a choroidal melanoma. While there is no one cause, choroidal melanoma is more common among patients with blue vs. brown eyes, those with outdoor occupations, and in Australia where there is a hole in the ozone layer. Therefore, though this hypothesis has yet to be proven, it seems reasonable to assume that choroidal melanoma is related to sunlight (ultraviolet exposure).
In that sunlight exposure has been linked to several eye cancers and diseases of the eye, Dr. Finger suggests that you “Think of Sunglasses as Sun Block for your Eyes” ™ and start wearing your UV blocking sunglasses. They make great gifts too!
Dr. Finger also often gets questions related to stage and spread. These two things are closely linked––choroidal melanoma size is most closely related to its risk for spread to other parts of the body (metastasis). In three separate studies, cumulatively involving almost 20,000 patients, the average rate of metastasis has been 50%. However, patients with smaller tumors have much lower rates compared to larger tumors. Therefore, patients should ask their eye cancer specialist about their tumors AJCC-UICC tumor size and risk for metastasis. In general, the larger the choroidal melanoma the worse the prognosis for both vision and metastasis.
Related links
- View photographs of choroidal melanoma, choroidal nevus and other choroidal tumors
- View ultrasound images of choroidal melanoma and other ocular tumors
- A comparison of plaque versus proton radiation for choroidal melanoma
- A comparison of iodine-125 versus palladium-103 eye plaque radiation therapy
- What some patients look like after enucleation for choroidal melanoma
- Read about the “Finger Classification of Radiation Retinopathy” and how it predicts vision loss.
- An overview of treatments for metastatic choroidal melanoma
- Images related to radiation therapy for choroidal melanoma
- An article about PET/CT to monitor for metastastic choroidal melanoma
- Why choroidal melanoma specialists should use a standardized classification “language.”
- Ocular prosthesis care after enucleation for choroidal melanoma
- Scientific articles about choroidal melanoma written by Dr. Finger
- The Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study (COMS): What is it? What did it show?
- Dr. Finger shows how three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound can be used to make sure the plaque is placed correctly
- Frequently asked questions about choroidal melanoma
- Frequently asked questions about enucleation for choroidal melanoma
- Other patients with choroidal melanoma can be found on our bulletin board
- Learn more about The New York Eye Cancer Center’s approach to treatment of choroidal melanoma
- To Treat or Not to Treat – The Small Choroidal Melanoma Controversy