Optic Nerve Melanocytoma
Description
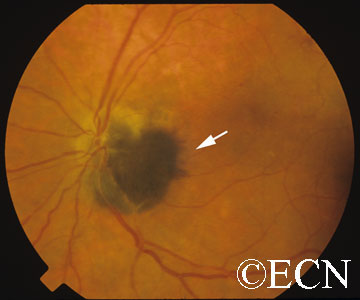
Optic nerve melanocytoma is typically a benign tumor made up of melanocytes and melanin. They can grow, but rarely transform into a malignancy. However, local growth can harm adjacent tissues.
Symptoms
Optic nerve melanocytoma does not usually produce symptoms or grow. If they slowly grow, optic nerve melanocytoma can produce afferent pupillary defects (30%), subretinal fluid (10%), and an enlarged blind spot (75%).
For example, if the tumor is next to the optic nerve, growth can compress the nerve and cause loss of vision (e.g. nerve fiber layer defects). Growth can also cause compressive vascular problems like central retinal vein occlusion. Lastly, growth also causes the tumor to exceed its blood supply. In these cases, necrotic areas form inside the tumor. Necrosis can (in turn) cause intraocular and rarely orbital inflammation.
Diagnosis
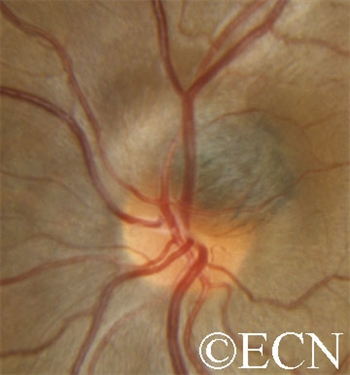
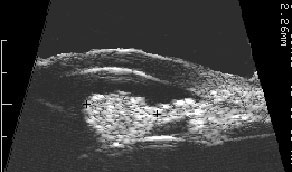
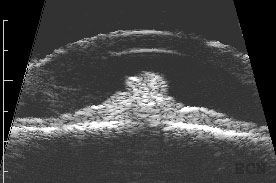
A medium-sized juxtapapillary melanocytoma
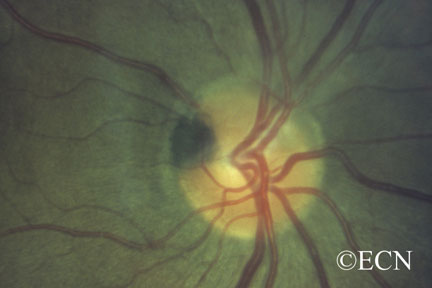
Unlike choroidal melanoma, optic nerve melanocytomas are black, commonly extend onto the surface of the optic nerve and invade the nerve fiber layer (feathered edge).
Treatments
Patients with optic nerve melanocytoma should have a visual field test, as well as a photograph of the optic nerve and tumor. These examinations can serve as a baseline for future comparison. Patients with optic nerve melanocytoma should be periodically examined for evidence of growth, loss of visual field and optic nerve compression.
Unfortunately, there are no current treatments to prevent or stop optic nerve melanocytoma growth. Patients are examined every 6 to 12 months with dilated ophthalmoscopy and visual field examinations as to counsel patients about the risk of vision loss, treat compression-related vasculopathy and monitor for the rare occurrence of malignant transformation.
Additional info
Though rare, tumor growth can lead to radiation or enucleation (removal of the eye).