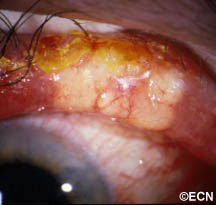
Sebaceous cell carcinoma is suspected due to evidence of eyelash loss and the formation of a yellow-nodule. This tumor can also present as a persistent (months) non-responsive blepharitis or conjunctivitis. In these cases, a high index of suspicion for sebaceous cell carcinoma will lead to biopsy and the diagnosis. Once sebaceous carcinoma is suspected a biopsy is warranted. Before surgery, the pathologist should be advised of this possible diagnosis so the specimen can be processed appropriately