By Paul T. Finger, MD
Description
Seborrheic keratosis is one of the most frequently noted benign eyelid tumors.
Symptoms
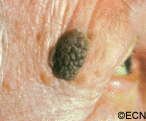
Unlike squamous carcinomas of the eyelid, seborrheic keratosis does not typically cause inflammation around its edges nor does it have a smooth reddened scaly surface. If it does become inflamed it can be mistaken for a basal or squamous cell carcinoma.
Diagnosis
Typical appearing seborrheic keratosis can be photographed and followed for evidence of change prior to consideration of biopsy or removal. Suspicious seborrheic keratosis can be differentiated from other eyelid tumors by a simple biopsy.
Treatments
Seborrheic keratosis does not require treatment. Photography should be used to document its initial size for future reference and comparison. Suspicious lesions should be biopsied or removed to differentiate them from malignant eyelid tumors.
Note its “stuck-on” appearance, its cobblestone surface, well-defined margins and lack of inflammation. Histopathology reveals a hyperkeratotic tumor consisting of a basaloid proliferation with keratin cysts.