By Paul T. Finger, MD
Description
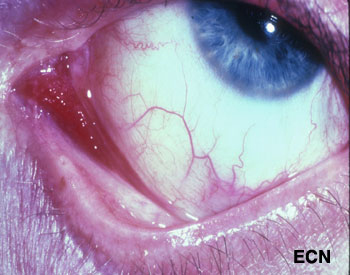
Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) can affect the conjunctiva and eyelids. It is a red to pink conjunctival tumor and a blue to purple eyelid tumor. In North America, it is typically found in patients with HIV acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), but can occur in the elderly and immunocompromised (e.g. transplant patients). Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma also occurs in the elderly and is slowly progressive.
Diagnosis
If the doctor suspects that a conjunctival tumor is Kaposi’s sarcoma, the patient’s skin and lymph nodes should be examined. Blood should be tested for HIV, lymphocytes, and other opportunistic diseases. One can make a tissue diagnosis based on a biopsy, or a presumptive diagnosis in patients with a history of Kaposi’s. One problem with a presumptive diagnosis (in this group of patients) is that these patients are particularly vulnerable to developing squamous and lymphoid conjunctival tumors.
Your eye care professional is more likely to suggest an incisional biopsy for diagnosis. In most cases, this can be performed in a treatment room with local anesthetic. Sterile technique, HIV precautions, and proper labeling of the specimen are required. In order to biopsy, it is not necessary to completely excise the Kaposi’s sarcoma (unless it is small and unifocal).
Treatments
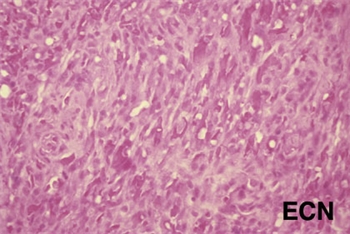
Treatment depends on the patient’s age, and the status of his or her general health, current medications and immune status. Small Kaposi’s sarcomas can be removed at biopsy. Larger and multifocal tumors are biopsied, proven Kaposi’s sarcoma by pathologic analysis, and treated (systemically or regionally).
Chemotherapy, radiation therapy and biologic therapy can be employed. In cases of HIV-AIDS related Kaposi’s sarcoma, we tend to avoid any treatment that would further suppress the patient’s immune system. If treatment of the patient’s underlying HIV-AIDS does not halt the progression of the Kaposi’s sarcoma, this tumor has been found to be very sensitive to external beam radiation therapy.
Additional Info
For the ophthalmologist who discovers conjunctival Kaposi’s sarcoma, it is important to coordinate care with a team consisting of a medical oncologist (and/or HIV-specialist), and radiation oncologist.