By Paul T. Finger, MD
Description
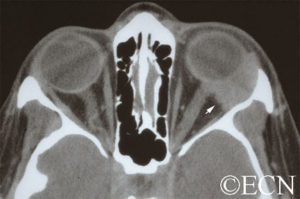
Orbital mucocele can occur when sinus mucoceles cannot naturally drain through the nose. Instead, they grow and slowly invade adjacent orbital tissues.
Generally arising from the ethmoid or frontal sinuses, orbital mucoceles are mucous or fluid filled cysts which can displace the eye. Frontal sinus mucoceles can force the eye down, ethmoid tumors will push the eye out and maxillary lesions can elevate or push the eye in. Lastly, orbital mucoceles originating in the sphenoid sinus can compress the optic nerve resulting in loss of vision.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
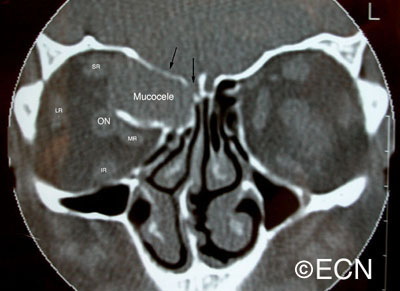
demonstrates displacement of the medial rectus muscle (MR), as well as erosion and obliteration of portions of the orbital roof (black arrows). Note that the orbital portion of the mucocele is partially encased in bone. This is characteristic of mucocele. The rectus muscles and optic nerve are labeled.
Though magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be consistent with a mucous or serous fluid-filled tumor, a drainage procedure is typically required and found to be diagnostic. The mucoid or serous fluid (which is found to make up the mucocele) should be sent for culture and sensitivity as well as cytologic examination. Mucoceles can be infected. In those cases, the choice of antibiotics can depend on cultures taken during surgery.
Treatments
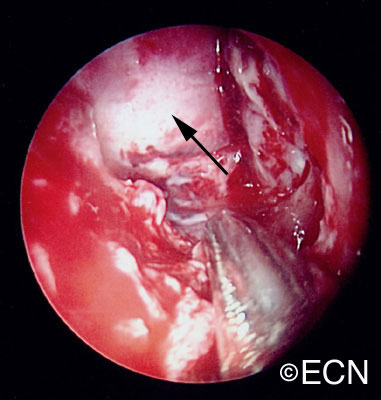
The treament of mucocele of the orbit is surgical. It is best to have a combination of an ophthalmic and ENT surgeons. Treatment involves removal of as much of the cyst and its lining as possible. This usually requires an orbitotomy and sinusectomy. It is most important to re-establish or create a new drainage pathway for the mucous to exit the nose.
Additional info
Case Example: A 63 year old male was referred to The New York Eye Cancer Center with a 6 month history of progressive painless proptosis of the right eye.
Despite this large orbital tumor with optic nerve displacement, the patient was 20/20 OU, he had no visual field defect, and no signs of optic neuropathy. A complete medical survey was initiated and the patient was cleared for surgery. A combination of anterior orbitotomy and transnasal ethmoidectomy were performed to evacuate the mucous and allow for future drainage.