A new study by Dr. Sonal Chaugule and Dr. Paul Finger has identified a promising treatment for patients diagnosed with iris melanoma. This is a first study describing regression characteristics in published literature.
Uveal melanoma is the most common primary intraocular malignancy in adults. Iris melanoma is the rarest cancer in this family, making up only 2% to 3% of cases. However, recent studies have found that biopsy-proven iris melanomas can spread outside the eye in up to 11% of cases. These findings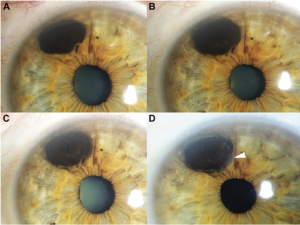 support the treatment of iris melanomas.
support the treatment of iris melanomas.
In the past, most patients with melanoma of the iris were treated by removal of the tumor along with the surrounding iris. Though the tumor is removed, the surgical procedure usually leaves a giant pupil with a non-functional iris sphincter and symptoms of glare.
“After part of the iris is removed, it is like having one pupil constantly dilated, even in the sun,” Dr. Finger said.
In their new study Chaugule and Dr. Finger describe patterns of tumor regression and side effects after iris-sparing treatment for iris melanoma using palladium-103 (103Pd) plaque brachytherapy. At the New York Eye Cancer Center, plaque brachytherapy has been found to be a conservative treatment modality with low local recurrence rate. Treatment with plaque radiation to sterilize the melanoma eliminates the need to open the eye, remove the tumor and make the pupil abnormally large.
Dr. Chaugule sought to examine and document the patterns of change after plaque radiation therapy for iris melanoma. The study included 50 patients with iris melanoma who underwent 103Pd plaque brachytherapy with at least 6 months of follow-up. Pre-treatment and post-treatment tumor morphology, gonioscopy and high frequency ultrasound imaging was studied and analysed.
In this study, palladium (103Pd) plaque brachytherapy of iris melanomas showed dissappearance of blood vessels within the tumor,, darkening of tumor surface, and decreased tumor thickness. With 100% local and systemic control at a mean duration of 5.2 years, the study shows this to be a safe and effective pupil sparing treatment.








That’s interesting that there is the treatment for melanoma in the iris. I always thought you could only get melanoma on your skin. I’ll have to check with a dermatologist if this is something I should be watching for.